Create Database Manually – Step by Step instruction
Posted by Kamran Agayev A. on 31st May 2009
Today, I’ll show you how we can create a Database without Database Configuration Assistant (DBCA). We’re going to create the database manually, using CREATE DATABASE statement. Sometimes, we are not able to use GUI in order to create a database. For this, we should know syntax of database creation from SQL*Plus. To create database manually, follow below steps:
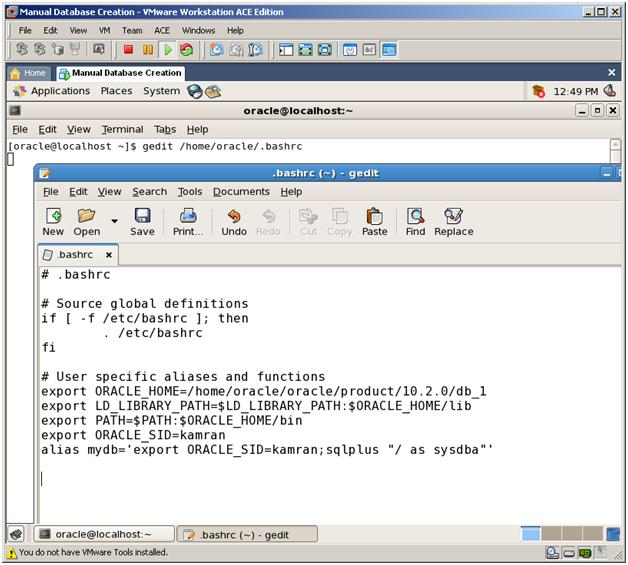
1. Firstly, export Environment Variables. To export EV automatically for every session, do below changes to /home/oracle/.bashrc file:
export ORACLE_SID=kamran
export ORACLE_HOME=/home/oracle/oracle/product/10.2.0/db_1
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:$ORACLE_HOME/lib
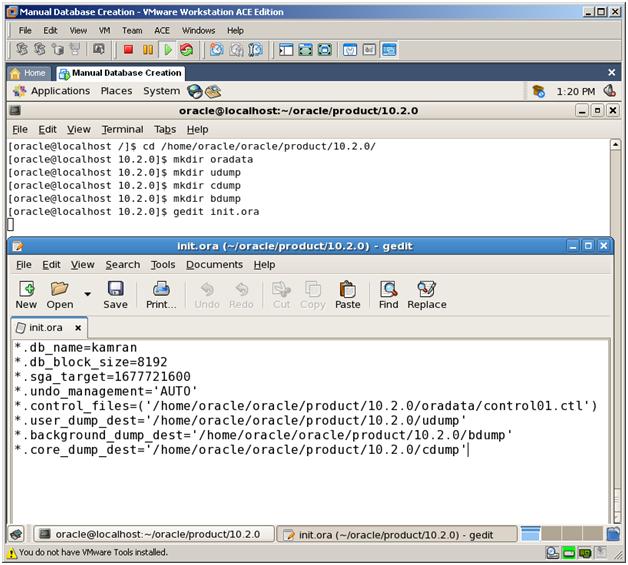
2. Create parameter file and modify it by setting minimum required parameters:
*.db_name=kamran
*.db_block_size=8192
*.sga_target=1677721600
*.undo_management=’AUTO’
*.control_files = (‘/home/oracle/oracle/product/10.2.0/control01.ctl’)
*.user_dump_dest=’/home/oracle/oracle/product/10.2.0/udump’
*.background_dump_dest=’/home/oracle/oracle/product/10.2.0/bdump’
*.core_dump_dest=’/home/oracle/oracle/product/10.2.0/cdump’
After creation of this parameter file, create below folders in /home/oracle/oracle/product/10.2.0/ directory. Three of them are dump folders (needed for trace files and alert.log file). We’re going to keep Control Files and DataFiles in oradata folder.
– oradata
– udump
– bdump
– cdump
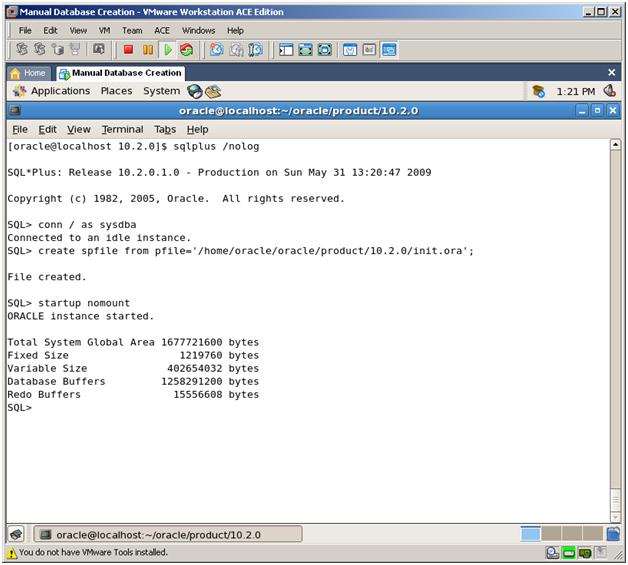
3. Create Server parameter file (SPFILE) using this parameter file and STARTUP the instance in NOMOUNT mode.
CREATE SPFILE FROM PFILE=’/home/oracle/oracle/product/10.2.0/init.ora’;
STARTUP NOMOUNT
Now our instance started, SGA allocated and background processes started
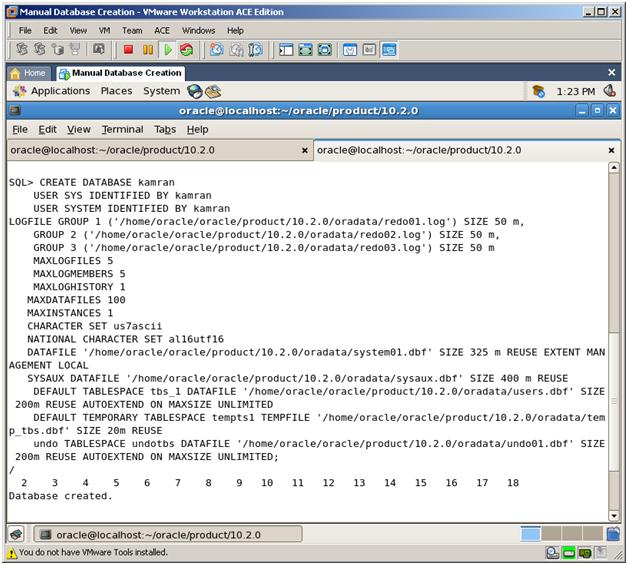
4. To create a new database, use the CREATE DATABASE statement. As a result, below files will be created:
– Redo Log files
– system.dbf and sysaux.dbf (files for SYSTEM tablespace)
– undo01.dbf file (for UNDO tablespace)
– temp_tbs.dbf file (for TEMPORARY tablespace)
– users.dbf (for DEFAULT PERMANENT tablespace)
//######## Database Creation Code #######
CREATE DATABASE kamran
USER SYS IDENTIFIED BY kamran
USER SYSTEM IDENTIFIED BY kamran
LOGFILE GROUP 1 (‘/home/oracle/oracle/product/10.2.0/oradata/redo01.log’) SIZE 50 m,
GROUP 2 (‘/home/oracle/oracle/product/10.2.0/oradata/redo02.log’) SIZE 50 m,
GROUP 3 (‘/home/oracle/oracle/product/10.2.0/oradata/redo03.log’) SIZE 50 m
MAXLOGFILES 5
MAXLOGMEMBERS 5
MAXLOGHISTORY 1
MAXDATAFILES 100
MAXINSTANCES 1
CHARACTER SET us7ascii
NATIONAL CHARACTER SET al16utf16
DATAFILE ‘/home/oracle/oracle/product/10.2.0/oradata/system01.dbf’ SIZE 325 m REUSE EXTENT MANAGEMENT LOCAL
SYSAUX DATAFILE ‘/home/oracle/oracle/product/10.2.0/oradata/sysaux.dbf’ SIZE 400 m REUSE
DEFAULT TABLESPACE tbs_1 DATAFILE ‘/home/oracle/oracle/product/10.2.0/oradata/users.dbf’ SIZE 200m REUSE AUTOEXTEND ON MAXSIZE UNLIMITED
DEFAULT TEMPORARY TABLESPACE tempts1 TEMPFILE ‘/home/oracle/oracle/product/10.2.0/oradata/temp_tbs.dbf’ SIZE 20m REUSE
undo TABLESPACE undotbs DATAFILE ‘/home/oracle/oracle/product/10.2.0/oradata/undo01.dbf’ SIZE 200m REUSE AUTOEXTEND ON MAXSIZE UNLIMITED
5. Run the scripts necessary to build views, synonyms, and PL/SQL packages
CONNECT / AS SYSDBA
SQL>@$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/catalog.sql
SQL>@$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/admin/catproc.sql
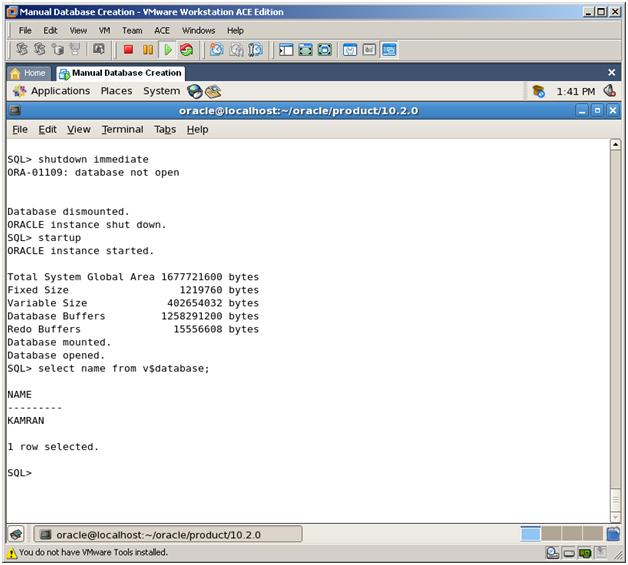
6. Shutdown the instance and startup the database. Your database is ready for use!
Posted in Administration, Oracle on Linux | 66 Comments »